
What is Swine Flu?
Swine influenza (also swine flu) refers to influenza caused by any virus of the family Orthomyxoviridae, that is endemic to pig (swine) populations. Strains endemic in swine are called swine influenza virus (SIV), and all known strains of SIV are classified as Influenzavirus A (common) or Influenzavirus C (rare).Influenzavirus B has not been reported in swine. All three clades, Influenzavirus A, B, and C, are endemic in humans.
People who work with poultry and swine, especially people with intense exposures, are at risk of infection from these animals if the animals carry a strain that is also able to infect humans. SIV can mutate into a form that allows it to pass from human to human. The strain responsible for the 2009 swine flu outbreak is believed to have undergone this mutation.
In humans, the symptoms of swine flu are similar to those of influenza and of influenza-like illness in general.
What are the symptoms?
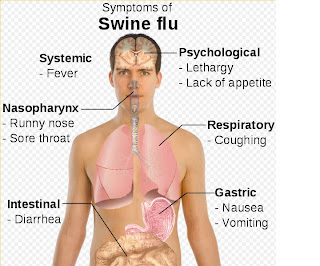
According to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in humans the symptoms of swine flu are similar to those of influenza and of influenza-like illness in general. Symptoms include fever, cough, sore throat, body aches, headache, chills and fatigue. A few more patients than usual have also reported diarrhea and vomiting.
Because these symptoms are not specific to swine flu, a differential diagnosis of probable swine flu requires not only symptoms but also a high likelihood of swine flu due to the person's recent history. For example, during the 2009 swine flu outbreak in the United States, CDC advised physicians to "consider swine influenza infection in the differential diagnosis of patients with acute febrile respiratory illness who have either been in contact with persons with confirmed swine flu, or who were in one of the five U.S. states that have reported swine flu cases or in Mexico during the 7 days preceding their illness onset." A diagnosis of confirmed swine flu requires laboratory testing of a respiratory sample (a simple nose and throat swab).
How to protect yourself and your family
Recommendations to prevent infection by the virus consist of the standard personal precautions against influenza. This includes frequent washing of hands with soap and water or with alcohol-based hand sanitizers, especially after being out in public. People should avoid touching their mouth, nose or eyes with their hands unless they've washed their hands. If people do cough, they should either cough into a tissue and throw it in the garbage immediately, cough into their elbow, or, if they cough in their hand, they should wash their hands immediately
Treatment
The CDC recommends the use of Tamiflu (oseltamivir) or Relenza (zanamivir) for the treatment and/or prevention of infection with swine influenza viruses. The virus isolates that have been tested from the US and Mexico are however resistant to amantadine and rimantadine.[31] If a person gets sick, antiviral drugs can make the illness milder and make the patient feel better faster. They may also prevent serious flu complications. For treatment, antiviral drugs work best if started soon after getting sick (within 2 days of symptoms).
Up to date map of spreading infection




No comments:
Post a Comment